Authors: Kiara Sitiriche & Gabriela Soto-Canetti
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects the way in which the body turns food into energy. Most of the food we eat is broken down into sugar, or glucose, and is released into the bloodstream. When blood sugar goes up, it signals the pancreas to release insulin. Insulin acts as a key to let blood sugar into the body to use as energy. If a person is diagnosed with diabetes, it means that the pancreas is no longer producing enough insulin or does not utilize insulin in the way it should. This causes raised glucose levels in the blood, also known as hyperglycaemia. Over time, diabetes can be the cause of more severe damages to the body.
There are three main types of diabetes and they should all be treated with the same amount of care and seriousness. Type 1 diabetes may develop at any age and is more common in children and young adults. This type of diabetes does not require daily insulin injections in order to maintain glucose levels under control. Type 2 diabetes is most common in adults and makes up around 90% of all diabetes cases. With Type 2 diabetes, the body does not use insulin as it should and over time, most people require insulin injections or prescribed drugs in order to give blood glucose levels under control. The third type of diabetes is gestational diabetes (GDM), only occurs during pregnancy and may cause complications in both mother and child. GDM disappears most times after pregnancy, but increases the risk of mother and child being diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes throughout their lifetime.
In order to effectively treat this condition, it is important to understand the severity of it and its underlying causes. It is for this reason that health professionals always recommend a lifestyle change to groups affected by diabetes. Healthy eating is key when certain foods can affect your blood sugar levels. Physical activity is another important part of managing your diabetes. Following we list some things that the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases recommends for a healthier lifestyle:
- Managing your ABC’S
- A for A1C Test. This test shows average blood glucose levels over the past 3 months. If a person has diabetes, they should ask their doctors what the percentage of their A1C Test should be.
- B for Blood Pressure. The blood pressure goal for most people is 140/90mm Hg, so it is important to ask a healthcare professional what an individual’s amount should be specifically. High blood pressure can be caused by diabetes, which underscores the importance of regularly checking your blood pressure if you have diabetes.
- C for Cholesterol. There are two types of cholesterol in blood, LDL (bad cholesterol) and HDL (good cholesterol). The HDL in the body can help remove the LDL from blood vessels. However, diabetes can lower HDL levels and raise LDL levels in blood vessels, meaning that patients should ask their doctor what their cholesterol numbers should be.
- S for Smoking. Smoking, as well as diabetes, narrows blood vessels. This means quitting smoking is an essential part of reducing the risk of future complications of diabetes.
- Following a personalized meal plan
- Drinking water instead of soda or sweetened beverages.
- Eating foods lower in calories and sugars.
- Eating chicken and turkey without the skin.
- Choosing fruits, vegetables, beans, and whole grains before anything else.
- Choosing non-fat or low fat dairy products.
- Increasing physical activity.
- Setting realistic physical goals.
- Working out at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Opting for walking and swimming as beginner options.
- Asking a doctor about how to improve physical activity.
In 2018, 34.2 million Americans reported having diabetes and 7.3 million of these remained undiagnosed. While diabetes is an incurable disease, there are evidence-based treatments and strategies that can be adopted to improve quality of life. The recommendations above are just a few of the strategies that can make it easier to deal with this disease. Adopting healthy behaviors has been proven to improve health outcomes and quality of life among those with diabetes. These behaviors may further contribute to avoiding complications of diabetes such as heart disease, nerve damage, vision loss, and kidney disease.
It is also of great importance to take care of medications to manage diabetes. In the case of Insulin users in particular, this medication needs to be stored below 8°C and above 2°, according to CDC guidelines. Most patients store their medications in their domestic refrigerators. However, fridges have temperature fluctuations that can affect the medication’s potency or cause spoilage. Therefore, it is recommended to keep constant track of the appropriate temperature range. Personal-use cooling systems, such as the one Insu Health Design is developing, can keep the medication protected at the right temperature for every-day use, travel or times of limited access to electricity.
Even if a person does not suffer from this disease, advocating for self-care and self-management to those with diabetes can be surprisingly beneficial. It is for this reason that we must all remain informed and aware of the effect this disease has on the larger population.
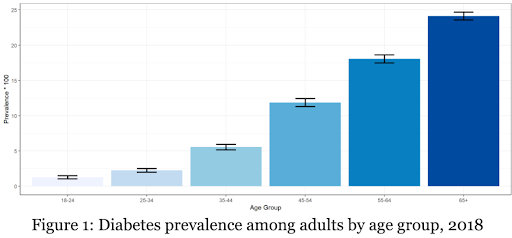
If you or someone close to you is diagnosed with diabetes, it is necessary to be aware and up to date with information and statistics surrounding this disease. If you are interested in learning more about how diabetes affects people nationwide, check out Matrix2Metrics for nationwide up to date data and reports.